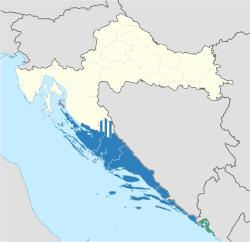
Travel & Tourist Information for Dalmatia
Please find the following links helpful in your arrangements this season:
Ministry of Tourism Republic of Croatia
Republic of Croatia Ministry of the Interior
National Protection and Rescue
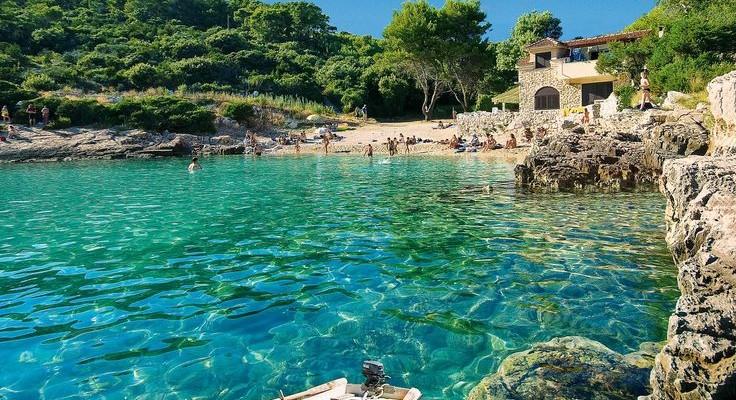
Geographic position
Croatia occupies the largest part of the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea which, as a part of the Mediterranean Sea, penetrates deepest into European soil. Croatia’s shoreline and numerous islands enjoy the majority of the Adriatic coastline. The narrow Dinara Mountain Range separates the country’s Mediterranean region from its central European continental part, which spans from the easterly edges of the Alps in the North-West to the shores of the Danube in the East, encompassing the southern part of the fertile Pannonian lowlands.
Climate: There are 3 climate zones in Croatia: in the country’s continental interior the prevailing climate zone is moderately continental , while the mountain climate prevails at 1200m above the sea level. The area along the southern Adriatic coast is known as ‘Dalmatia‘ and has a pleasantly mild Mediterranean climate with a large number of sunny days, summers are hot and dry and winters are mild and wet. The average temperatures in the continental interior are: January -2 oC to 0 oC, with somewhat lower temperatures in the mountains; July temperatures reach 20 oC-22˚C, and around 13˚C in the highlands. The average temperatures in the Littoral (Adriatic Coast) are: January 5˚C – 9 oC and July 23°C – 26°C. Winter sea temperature is about 12 oC and it reaches approximately 25 oC in the summer.
Information: www.meteo.hr
Currency
As of January 2023, the currency used in Croatia is the Euro. Prior to this change, Croatia’s official currency was the Croatian Kuna (HRK) between 1994 and 2023. Foreign currency can be exchanged in banks, exchange offices, post offices, and the majority of tourist information offices, hotels, and campsites. Credit cards (Eurocard, Mastercard, Visa, American Express and Diners) are accepted in almost all hotels, marinas, restaurants, shops and cash machines.
Travel documents
A valid passport or some other identification document recognized by international agreement is sufficient; for certain countries, a personal identity card is sufficient (a document that testifies to the identity and citizenship of the bearer). Information: Diplomatic missions and consular offices of the Republic of Croatia abroad or the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and European Integration of the Republic of Croatia
Customs Regulations
Customs regulations when you travel to the Republic of Croatia are almost entirely harmonised with EU regulations and standards, but the value of those non-commercial items that are brought into the country for personal use and are exempt from tax duty or PDV (VAT), is limited to only 1,000 HRK (kuna). Foreign and local currency and cheques may be freely taken in and out of the country by both foreign and Croatian citizens with foreign residence, but transfers of an amount of 10,000 Euros or more must be declared to a customs official. Valuable professional equipment and other technical devices must also be declared to a customs official at the border crossing. VAT is refunded to persons who do not have permanent or temporary residence in Croatia, for individual goods purchased in Croatia, for amounts in excess of 740.00 HRK (Kuna), upon the presentation of a Tax Cheque form verified by a customs official during the export of purchased goods, at the latest 3 months from the day of purchase. Foreign nationals must claim Tax refunds within six months of the receipt issue date.
CROATIA FACTS:
Surface area: The mainland covers an area of 56 594 km2 and coastal waters cover a surface area of 31 479 km2.
Population: Croatia has 4 290 612 inhabitants.
Demographics: The majority of the population are Croats, with the largest minorities being Serbs, Bosnians, Slovenes, Hungarians, Czechs, Italians and Albanians.
System of government: Croatia is a multi-party parliamentary republic.
Capital: With 792 875 inhabitants, Zagreb is the economic, transport, cultural and academic centre of the country.
Length of the coastline: 6 278 km, of which 4 398 km is made up of island coastlines, solitary rocks and reefs.
Number of islands, islets, solitary rocks and reefs: 1,244. The largest islands are Krk and Cres. There are 50 inhabited islands.
Highest peak: Dinara, 1 831 m above sea level.
Brief Historical Facts:
Dalmatia (/dælˈmeɪʃə/; Croatian: Dalmacija, Croatian pronunciation: [dǎlmaːt͡sija]; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria.
In 1848, the Croatian Assembly (Sabor) published the People’s Requests, in which they requested among other things the abolition of serfdom and the unification of Dalmatia and Croatia.
The Middle Ages in Dalmatia were a period of intense rivalry among neighboring powers: the waning Byzantine Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (later in a personal union with Hungary), the Bosnian Kingdom, and the Venetian Republic.
In antiquity the Roman province of Dalmatia was much larger than the present-day Split-Dalmatia County, stretching from Istria in the north to historical Albania in the south.
Much later, the region was settled by Liburnians and Illyrians, while the first Greek colonies were established on the islands of Korčula, Hvar and Vis.
Roman survivors retreated to more favourable sites on the coast, islands and mountains.